-
ene 30
Parrondo's Paradox
Parrondo's Paradox¶
A fun hands-on example to understand Markov Models.
Introduction¶
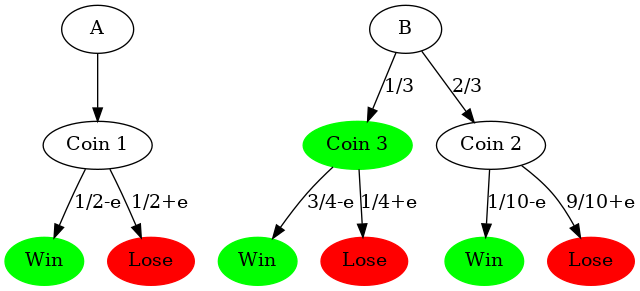
Parrondo's paradox is a mind-blowing mental experiment in which the combination of two different losing games can become in a wining one. $$ L_{ose} + L_{ose} = W_{in}?$$
There's a lot of interesting literature around it. You can search for it in the internet, but I'll just explain the most simple example in terms of two games played with biased coins.
-
jul 04
Send notifications to your phone with PushJet
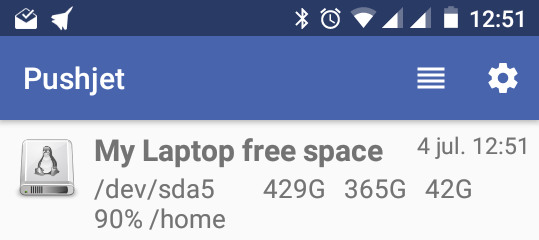
Recently, I've faced the need of monitoring some basic checks in my laptop and wanted to be rapidly notified about them. Basically I have a small script scheduled in my crontab and want it to clearly notify me when it returns errors. My real task was a little bit more complicated, but let's say I just wanted to check the free space on root partition.
-
feb 02
PI4fun (Part 2)
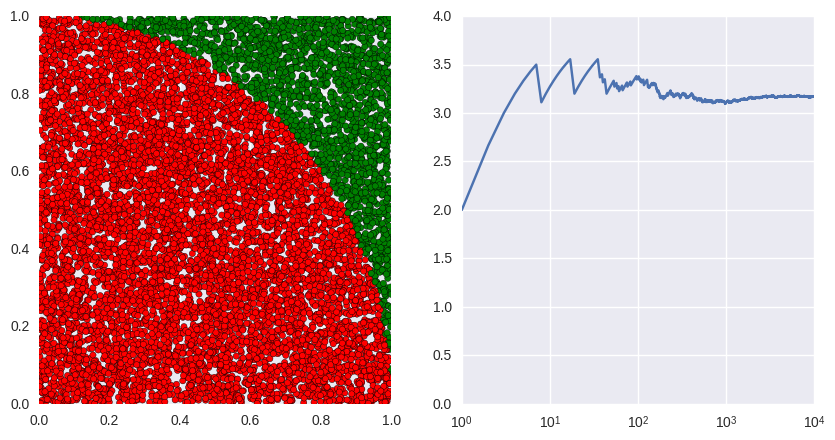
Estimating $\pi$ for fun (Part 2: illustrating the process)¶
In previous post we could see how to estimate $\pi$ value with a simple Monte Carlo algorithm.
Now we're going to illustrate the process with some simple plots.
Let's remember the code we prevously had:

-
ene 31
Cache your properties with a decorator
This is a wonderful Python idea I've found quite usefull and fun to implement.
The reason of the need comes from an analytics project I'm working on.
I have to read data from several sources (let's think on a file, a database or a remote query) that changes at predefined periods (let's say each minute).

-
ene 30
Ola de ataques de ransomware: ¿pone en entredicho la seguridad de MongoDB y otras bases de datos libres?
Se están leyendo estos días multitud de noticias acerca de ataques ransomware a determinadas bases de datos como Hadoop, ElasticSearch, Couchdb o MongoDB y en algunos medios se relacionan los ataques con el hecho de que se trate en todos esos casos de productos de software libre.
Relacionar los recientes ...

-
dic 05
PI4fun (Part 1)
Estimating $\pi$ for fun (Part 1: the basics)¶
The proposed project in this article is an example I tend to use in my Python introductory courses. The purpose is to calculate a dummy PI estimation based on a damn simple Monte Carlo algorithm.
It’s a simple and fun example that can be approached in a really direct and simple way, but that can be improved in many ways.
Page 1 / 2 »